The common bed bug (Cimex lectularius) is more than just an annoying household pest; it’s a stealthy invader that can cause great discomfort and distress. To eradicate an infestation effectively, it is essential to grasp the intricacies of the bed bug life cycle. This in-depth guide sheds light on the different stages of a bed bug’s life and provides practical, research-backed advice on stopping an infestation in its tracks.
The Bed Bug Life Cycle: From Egg to Adult
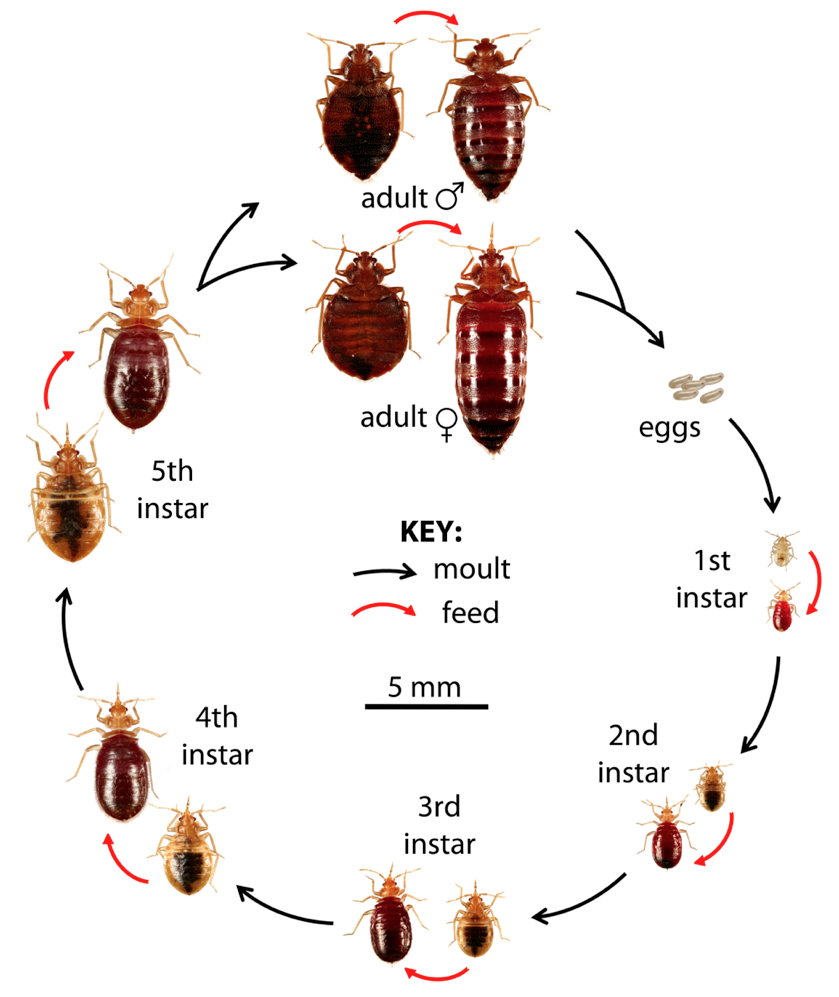
Bed bugs undergo a process called hemimetabolous metamorphosis, meaning they have three main stages in their life cycle: egg, nymph, and adult. Here’s a detailed overview:
Stage 1: Eggs
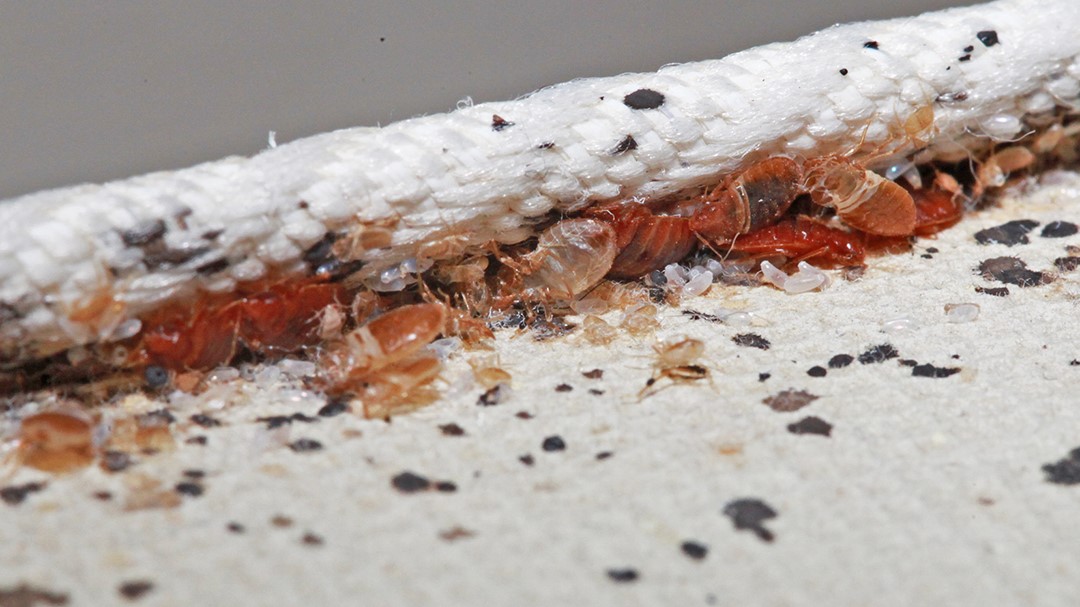
A female bed bug can lay up to 500 eggs in her lifetime, typically depositing them in dark, hidden areas. These eggs, about the size of a pinhead, hatch within one to two weeks, giving rise to the next stage: nymphs.
Stage 2: Nymphs
Once hatched, the immature bed bugs, called nymphs, immediately start to feed. They go through five moulting stages, requiring a blood meal before each moult. Under favourable conditions, this stage can be completed in as little as five weeks.
Stage 3: Adults
The final stage of the life cycle is the adult bed bug, which is about the size of an apple seed. Adults are extremely resilient and can live for nearly a year, feeding and reproducing throughout this time.
Unmasking the Bed Bug: Recognizing Signs of Infestation
Being able to identify bed bugs at different stages of their life cycle is crucial for effective infestation management. Look for these signs:
- Physical presence of bugs: This is the most evident sign. Adult bed bugs have a reddish-brown colour and a flat, oval-shaped body.
- Blood spots on bedding: As bed bugs feed, they often leave behind small blood spots on your sheets.
- Faecal spots: These tiny dark spots are often found in the areas where bed bugs hide during the day.
- Cast skins: As nymphs grow, they shed their skin, leaving behind a clear sign of infestation.
Breaking the Cycle: Effective Bed Bug Control
Understanding the life cycle of bed bugs paves the way for effective pest control strategies. Here are some proven measures:
1. Comprehensive Inspection
A thorough inspection is the first step. It’s essential to identify all infested areas to target the pest at all life stages. Consider hiring a professional pest control service for this task..
2. Pesticide Application
When dealing with extensive infestations, using insecticides can be an effective control measure. However, use these products judiciously and always follow label instructions. Some bed bug populations have developed resistance to certain insecticides, so a combination of products may be required.
3. Prevention Strategies
Prevention is always better than cure. Regularly inspect your living space, avoid bringing second-hand furniture into your home without a thorough check, and consider using bedbug-proof mattresses and box spring encasements.
By understanding the bed bug life cycle and adopting a comprehensive, multi-pronged approach to pest control, you can keep your home bed bug-free. Remember, the battle against bed bugs is one best fought with knowledge, patience, and persistence.
Understanding Bed Bug Behavior
To truly conquer a bed bug infestation, we need to delve deeper into the bed bug’s behavioural patterns. This knowledge will provide additional, practical insights for managing these pests.
Nocturnal Feeding: The Bed Bug’s Stealthy Meal Time
Bed bugs are primarily nocturnal creatures, with peak activity just before dawn. Drawn by warmth and carbon dioxide, they typically feed on sleeping humans, making their living environments prime feeding grounds.
Choosing Their Habitat: Bed Bug Preferences
Bed bugs are not limited to beds as their name might suggest. They are known to inhabit a wide range of spaces within the human environment, including furniture, cracks in walls, and under carpets. Remember this when conducting inspections and treatments.
Reproduction: Rapid Expansion of Bed Bug Populations
A female bed bug lays one to five eggs each day, leading to rapid population growth if left unchecked. Understanding this reproduction rate underscores the urgency of quick, decisive action once an infestation is detected.
Survival Tactics: Bed Bug Resilience
Bed bugs are renowned for their resilience. They can survive for months without feeding and resist temperature extremes. This resilience makes thoroughness and persistence key in any eradication efforts.
Taking Action: A Step-by-Step Guide to Managing Bed Bug Infestations
Armed with this knowledge of bed bug life cycle and behaviour, it’s time to take decisive action. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
Step 1: Confirm the Infestation
Before taking any action, ensure that the pest in question is indeed a bed bug. Misidentification can lead to ineffective treatment and unnecessary expenses.
Step 2: Identify Infested Areas
Conduct a thorough inspection of the living space, paying close attention to sleeping areas and dark crevices. Remember, bed bugs can hide in the most unlikely places.
Step 3: Implement Treatment
Depending on the extent of the infestation, treatment may include heat treatment, insecticide application, vacuuming, or a combination of these. Always follow safety precautions when using pesticides.
Step 4: Monitor and Follow-up
After the initial treatment, continued monitoring is crucial to ensure complete eradication. Repeat treatments may be necessary.
The journey to a bed bug-free home can be challenging, but with a clear understanding of these pests and a methodical approach, success is within reach. Stay informed, stay vigilant, and take decisive action.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How long does the bed bug life cycle last?
The bed bug life cycle from egg to adult takes about five weeks under favourable conditions. However, the lifespan of an adult bed bug can be nearly a year.
2. How do I know if I have a bed bug infestation?
Signs of a bed bug infestation can include the physical presence of bugs, blood spots on bedding, faecal spots in hiding areas, and cast skins from moulting nymphs.
3. What are the effective methods for controlling bed bug infestations?
Effective control methods include comprehensive inspection, heat treatment, pesticide application, and proactive prevention strategies. A multi-pronged approach is usually the most effective.
4. When are bed bugs most active?
Bed bugs are primarily nocturnal, with peak activity just before dawn. They typically feed on sleeping humans.
5. Can bed bugs survive without feeding?
Yes, bed bugs can survive for several months without feeding, contributing to their resilience and making thorough eradication efforts necessary.
6. How fast can a bed bug infestation spread?
A female bed bug lays one to five eggs each day, leading to rapid population growth if left unchecked. This highlights the importance of swift action once an infestation is detected.
7. What steps should I follow to manage a bed bug infestation?
The key steps are: to confirm the infestation, identify infested areas, implement appropriate treatment, and then monitor and follow up to ensure complete eradication.
You may also enjoy reading this article
Was This Article Helpful?
- Please provide feedback and comments to help us improve our content.
- Share your experiences and any additional tips you have for dealing with pests.
Share this Post



